

The Korean alphabet was invented in the years 1443-46 by King Sejong of the Chosun dynasty. It is the only true alphabet native to the Far East. Korean is not related to Chinese, although it has used the Chinese characters, together with the Korean alphabet, for many centuries. (70% of the vocabulary comes from Chinese.)


The alphabet is known as “Hangul” in South Korea and “Chosungul” in North Korea. Overall, there are 2,350 Hangul symbols!

The letters are combined into syllable blocks. (Each Korean syllable is written in a block which was once represented by a Chinese character.) The sound of some consonants changes depending on whether they appear at the beginning or end of a syllable.
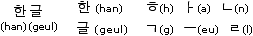
As is true for the Latin-script languages, words can contain several syllables and spaces are inserted between the words.
Korean is generally written horizontally from left to right but can also be written vertically from right to left.
The shapes of the vowels are based on three elements: man (a vertical line), earth (a horizontal line) and heaven (a dot). The dot became a short line.
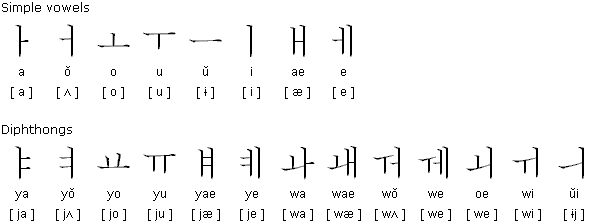
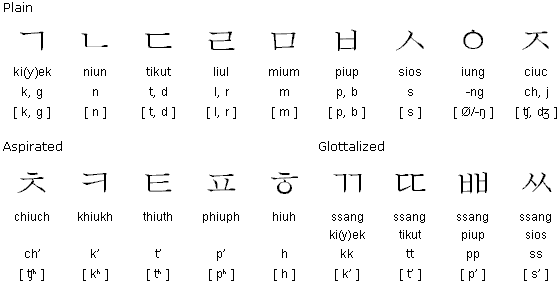
The shapes of some consonants are graphical representations of the speech organs used to pronounce them! Other consonants were created by adding extra lines to the basic shapes.
Which languages can OCR software read? — The history of the alphabets – Latin alphabet — Latin punctuation — Greek alphabet — Cyrillic (Russian) alphabet — Hebrew alphabet — Arabic alphabet — Let’s go East – Chinese alphabet — Japanese alphabet — Korean alphabet — Asian punctuation
Home page — Intro — Scanners — Images — History — OCR — Languages — Accuracy — Output — BCR — Pen scanners — Sitemap — Search — Contact – Feedback